WESTERN CPE BLOG
Providing the latest tax news, information, and updates for tax and finance professionals
How to Become a Certified Financial Planner
When it comes to occupying the throne in the land of accounting, and auditing, Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) have that covered. But who rules in the land of financial planning? Well, that would be the Certified Financial Planner, or CFP for short.
If you’re interested in financial planning or financial consulting, getting a CFP certification may be the next step to take. Let’s explore how to become a certified financial planner including the duties of a CFP, the CFP board, and taking the CFP exam to get your CFP certification.
What Does a CFP Do?
A Certified Financial Planner (CFP) is a financial professional who has earned the CFP certification from the Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards (CFP Board), and they do more than just offer financial advice. With their training to provide comprehensive financial planning advice to individuals, families, and businesses, they are able to assist with a wide range of financial matters, including the following: retirement planning, investment management, tax planning, insurance planning, and estate planning.
In addition, CFAs also help clients navigate complex financial decisions and provide guidance on how to achieve their financial goals. By assessing a client’s financial situation and goals, they can develop a personalized financial plan to accomplish and provide guidance along the way.
The Duties of a CFP
Because of their comprehensive knowledge of financial planning in a large variety, a CFPs duties can vary based on what their clients’ needs. Let’s break down some of the financial matters we mentioned above.
Financial Planning
CFPs can help clients set their retirement goals by estimating the cost of the client’s retirement based on the age they wish to retire and the lifestyle they wish to maintain during retirement. By estimating the cost of retirement, CFPs can create a plan to help achieve their client’s goals.
Investment Management
Some clients need assistance managing their investments to achieve financial goals. Advising their clients on asset allocation, diversification, and risk management can maximize returns while minimizing risk. CFPs can assist in selecting appropriate investments based on their financial goals, risk tolerance, and other factors.
Tax Planning
There are various financial decisions that can impact one’s taxes, including their investments. CFPs can help minimize their clients’ tax liability by providing tax planning strategies to guide them towards the right financial decisions.
Insurance Planning
Choosing the right insurance products can help protect a client and their families. Insurance needs can include life insurance, disability insurance, long-term care insurance, and other types of insurance. CFPs can help their clients choose the right products tailored to their needs.
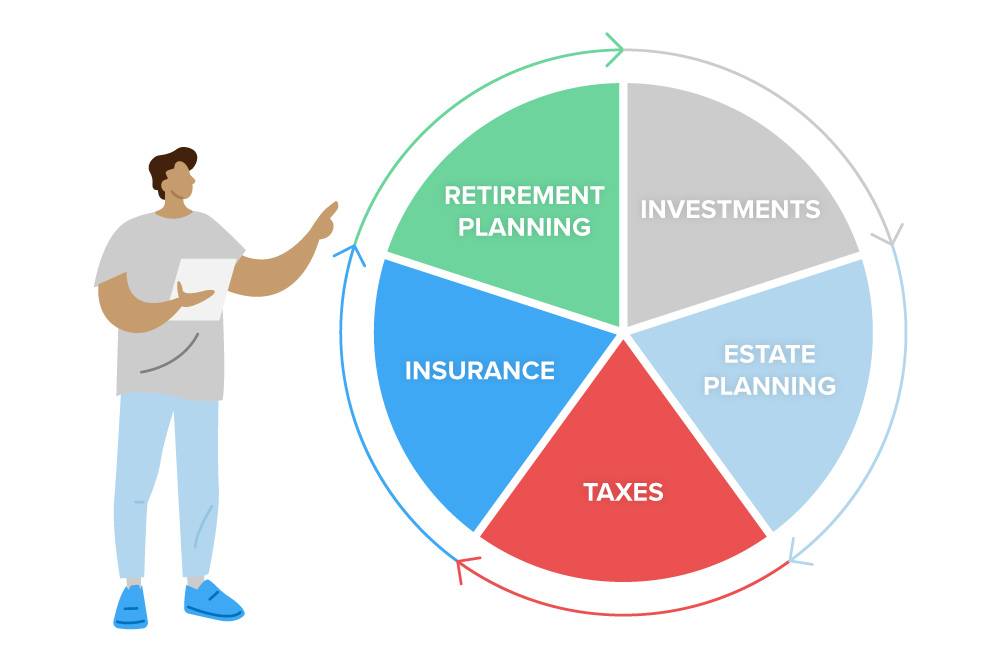
There are even more financial matters CFPs can help with in addition to those above. Since the area of financial consultation is broad and complex, some planners may choose to specialize in specific areas to help a particular kind of client.
The Importance of the CFP Board
Founded in 1985, the CFP Board, or the Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards, oversees the certification and regulation of CFPs in the United States. The board set the standards for CFP certification and is responsible for ensuring that CFPs adhere to a code of ethics and practice standards. The board is made up of various committees and task forces responsible for specific functions such as:
- Setting the standards for CFP certification
- Administering the CFP exam
- Regulating CFP professionals and their certifications
- Providing continuing resources to CFP professionals
What You’ll Need to Become A CFP
Now, here’s where the importance of the CFP Board comes to play. To become a CFP, an individual must meet the education, exam, experience, and ethics requirements established by the board. This is also known as the CFP Board’s “4 E’s” of CFP®.
The Education
A qualifying candidate must have completed a CFP Board-registered education program or have a bachelor’s and/or master’s degree in finance, accounting, business, or other related field.
The Exam
The candidate must pass the CFP Exam, which is broken down by the CFP Board as “a 170-question, multiple-choice test that consists of two 3-hour sessions over one day. The exam includes stand-alone and scenario-based questions, as well as questions associated with case studies.”
The exam is made to prove an individual’s knowledge in all aspects of financial planning to ensure skill and professionalism. It is offered in three eight-day windows: March, July, and November. There are also required registration fees: a standard registration rate is $925, an early bird rate of $825 is available, and a late registration rate of $1,025.
The Experience
To gain real-world experience, completing at least three years of full-time, relevant personal financial planning experience, two years of an apprenticeship under a CFP professional is highly recommended.
The Ethics
All CFP applicants must agree to abide by the CFP Board’s Standards of Professional Conduct and undergo a background check. Once this is complete, the full CFP certification can be submitted including proof of education, exam results, experience, and other qualifications.
The Future of CFPs
After obtaining a CPA certification, CFPs are required to complete ongoing continuing education to maintain certification. Career advancements can also become available by obtaining a master’s degree or more field related certifications.
According to a 2021 assessment conducted by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there is a 15% projected growth in employment personal financial advisors from 2021 to 2031. In addition, IBISWorld shows the financial planning market’s worth at $59.3 billion in 2022 with an average yearly growth of 3.4%.
In a such a growing and stable market with room for advancement, financial planning and consulting may be a kickstart career for those interested in a money-related field.
-
Self-Study
The Risk of Abuse in Accounting Estimates: GAAP Insights and Audit Strategies
$58.00 – $78.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Self-Study
Essentials of Nonprofit Fundraising
$232.00 – $262.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Self-Study
Pricing for Profit
$87.00 – $107.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page








